ClickHouse and Friends (10) MergeTree Write-Ahead Log
Last updated: 2020-09-18
Database systems write data to memory first to improve write performance, then flush to disk after “accumulating” to a certain extent. For example, MySQL’s buffer pool mechanism.
Because data is written to memory first, we need a Write-Ahead Log (WAL) to ensure the safety of in-memory data.
Today let’s look at ClickHouse’s newly added MergeTreeWriteAheadLog module and what problem it actually solves.
High-Frequency Write Problem
For the ClickHouse MergeTree engine, each write (even 1 row of data) creates a partition directory (part) on disk, waiting for the merge thread to consolidate.
If there are multiple clients, each writing small amounts of data frequently, this triggers a DB::Exception: Too many parts error.
This places requirements on clients, such as needing to do batch writes.
Alternatively, write to the Buffer engine and periodically flush back to MergeTree. The downside is potential data loss during crashes.
MergeTree WAL
1. Default Mode
Let’s first see how MergeTree writes without WAL:
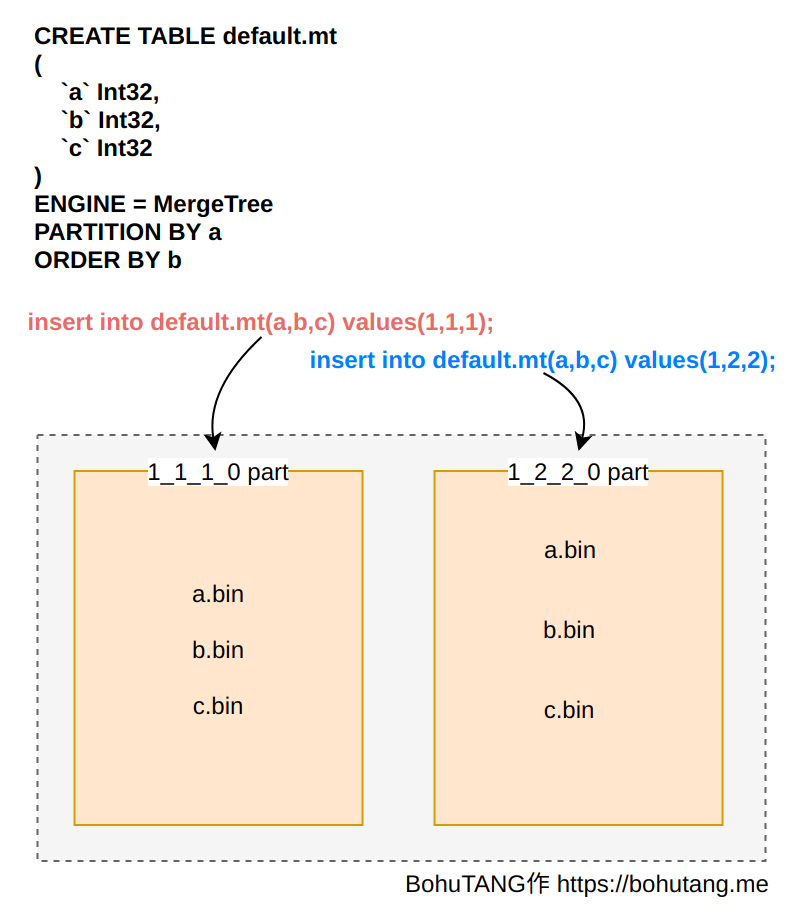
Each MergeTree write directly creates a partition directory on disk and generates partition data. This mode is essentially a fusion of WAL + data.
Obviously, this mode isn’t suitable for frequent writes. Otherwise, it generates too many partition directories and files, triggering the Too many parts error.
2. WAL Mode
Set SETTINGS: min_rows_for_compact_part=2. Execute 2 write SQLs separately. Data is first written to the wal.bin file:
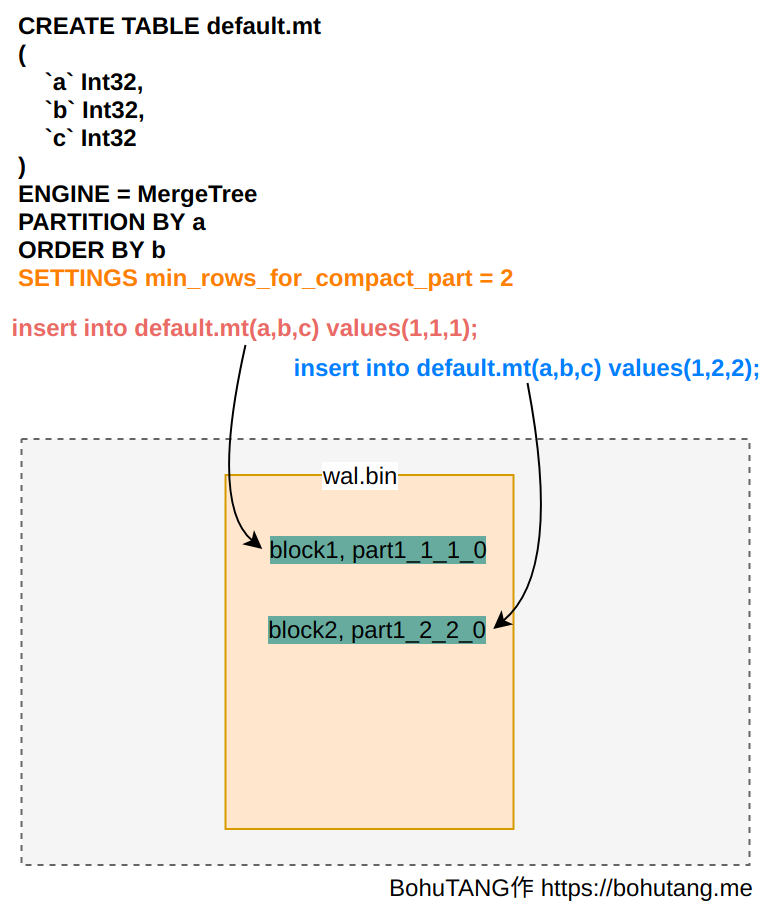
After meeting min_rows_for_compact_part=2, the merger thread triggers a merge operation, generating partition 1_1_2_1. This completes the merge of partitions 1_1_1_0 and 1_2_2_0 in wal.bin. When we execute the third SQL write:
1 | insert into default.mt(a,b,c) values(1,3,3) |
The data block (partition) continues appending to the tail of wal.bin:
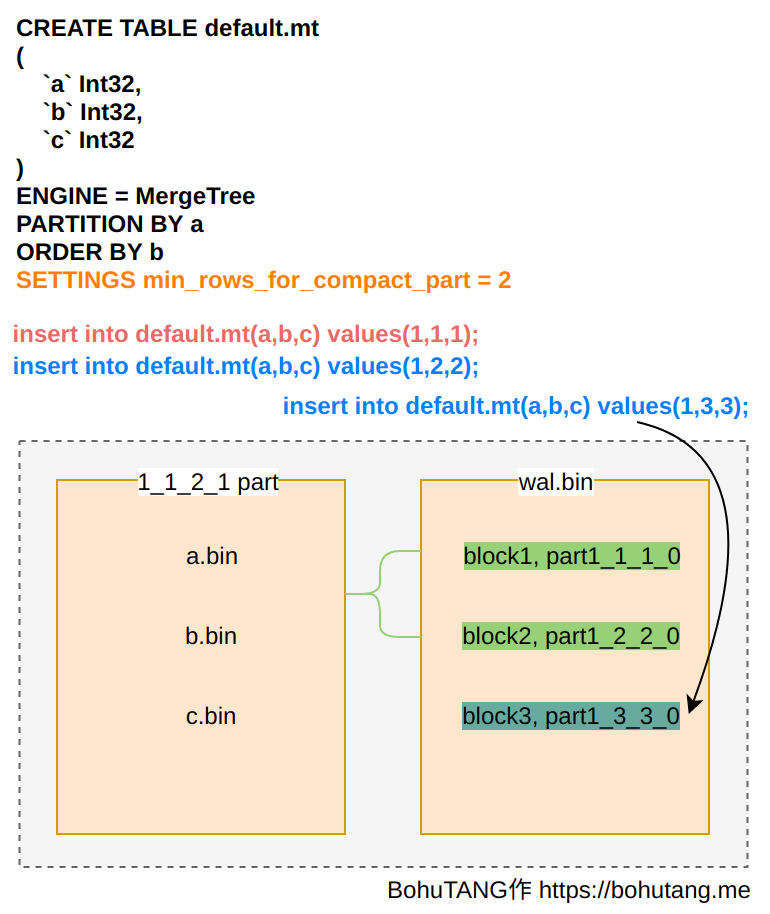
At this point, the 3 rows of data are distributed in two places: partition 1_1_2_1 and 1_3_3_0 in wal.bin.
This raises a question: when we execute a query, how is the data merged?
MergeTree maintains partition information using the global structure data_parts_indexes. When the service starts, the MergeTreeData::loadDataParts method:
1 | 1. data_parts_indexes.insert(1_1_2_1) |
This way, it can always maintain global partition information.
Summary
The WAL feature was implemented in PR #8290 and is now enabled by default in the master branch.
MergeTree uses WAL to protect clients’ high-frequency, low-volume write mechanisms, reducing server-side directory and file counts to keep client operations as simple and efficient as possible.